Unveiling the Power of Economic Indicators: Examining the Significance of the Unemployment Indicator
Understand how employment-related economic figures like the US non-farm payrolls can indicate the relative health of a national economy, and point to less or more demand for its currency.
Written by Aaron Akwu, Head of Education Hantec Markets
What is unemployment and its types?
Unemployment is a crucial economic indicator that reflects the number of people who are actively seeking employment but are unable to find work. It is measured through various metrics, such as the unemployment rate, which is calculated as the percentage of the labour force that is unemployed.
Types of unemployment
Understanding the different types of unemployment is essential in comprehending the dynamics of the labour market and formulating appropriate policies to address it. Let's look into the three main types of unemployment:
- Frictional Unemployment: Frictional unemployment occurs when individuals are temporarily unemployed while transitioning between jobs or entering the labour market for the first time. It is characterized by a short-term unemployment period due to factors such as job searching, relocation, or waiting for the right job opportunity. Frictional unemployment is a natural part of a healthy labour market as it allows workers to find better-suited employment options and helps employers match their requirements with suitable candidates.
- Structural Unemployment: Structural unemployment arises from a mismatch between the skills and qualifications possessed by workers and the demands of the labour market. This type of unemployment is often a result of technological advancements, changes in market preferences, or shifts in the overall structure of industries. When certain jobs become obsolete or new industries emerge, workers may find themselves unemployed if their skills are not aligned with the new demands. Addressing structural unemployment requires efforts such as retraining programs, educational initiatives, and promoting skill development to ensure workers can adapt to changing market conditions.
- Cyclical Unemployment: Cyclical unemployment is closely tied to fluctuations in the business cycle and occurs during economic downturns or recessions. When the overall economic growth slows down or contracts, businesses may reduce their workforce to cut costs, leading to a rise in unemployment. Conversely, during periods of economic expansion, cyclical unemployment decreases as businesses expand their operations and hire more workers. Governments and central banks often implement counter-cyclical policies, such as fiscal stimulus or monetary easing, to mitigate cyclical unemployment and promote economic growth.
Understanding the different types of unemployment helps policymakers and economists devise strategies to address specific issues within the labour market. By closely monitoring unemployment statistics and analyzing the unemployment rate measures, policymakers can assess the effectiveness of their policies and make informed decisions to foster job creation, support economic growth, and ensure the well-being of the labour force.
Unemployment Rates and Indicators
Unemployment rates and indicators play a crucial role in assessing the economic health of a nation. This will guide us into the intricacies of measuring unemployment rates, various calculation methods such as U-3 and U-6, the significance of the labour force participation rate, and the impact of underemployment. By exploring these aspects, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the factors that shape the employment landscape.
Measuring Unemployment Rates:
Measuring unemployment rates requires careful consideration and the use of reliable indicators. Governments and statistical agencies employ various methods to gauge the number of individuals without gainful employment. The most commonly used measure is the U-3 unemployment rate, which represents the percentage of people who are actively seeking employment but are currently jobless. It is often regarded as the official unemployment rate and provides a baseline for understanding the state of the labour market.
Calculation Methods - U-3 and U-6:
The U-3 unemployment rate, while widely referenced, does not capture the complete picture of unemployment. To address this limitation, the U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics developed the U-6 measure, which includes not only the unemployed individuals counted in U-3 but also those who are marginally attached to the labour force and part-time workers who would prefer full-time employment. The U-6 rate presents a broader perspective on the underutilization of labour resources and provides valuable insights into the extent of labour market slack.
Labour Force Participation Rate:
The labour force participation rate is a crucial indicator that complements the unemployment rate analysis. It represents the percentage of working-age individuals who are either employed or actively seeking employment. This rate considers not only the number of unemployed individuals but also those who have temporarily withdrawn from the labour force due to discouragement or other factors. The labour force participation rate can indicate changes in economic conditions, such as people rejoining the labour force during periods of economic recovery.
Impact of Underemployment:
While unemployment rates provide valuable insights, they often fail to capture the full spectrum of labour market challenges. Underemployment refers to a situation where individuals are employed in jobs that are below their skill level or are working fewer hours than desired. This phenomenon can have detrimental effects on both individuals and the economy as a whole. Underemployment can lead to reduced productivity, lower wages, and decreased job satisfaction. It can also hinder economic growth and impede the optimal utilization of human capital.
Seasonally Adjusted Rates:
When analysing unemployment rates and indicators, it is essential to consider seasonally adjusted data. Seasonal fluctuations, such as holiday-related employment spikes or agricultural cycles, can distort the accuracy of raw data. By applying seasonal adjustments, statisticians can account for these predictable patterns and provide a clearer representation of underlying trends and changes in the labour market.
Impact of Unemployment on Forex Market
Unemployment rates play a significant role in shaping the dynamics of financial markets, including the foreign exchange (forex) market. This segment will explore the relationship between unemployment and currency value, the effect of high unemployment on exchange rates, and the correlation between unemployment and interest rates.
- Relationship between Unemployment and Currency Value:
Unemployment levels can have a direct impact on the value of a country's currency in the forex market. When a nation experiences high unemployment rates, it often indicates a weakened economy and reduced consumer spending. Thi
s lack of economic activity can lead to a decrease in demand for the country's goods and services, resulting in a decline in exports and, consequently, the value of its currency.
Moreover, high unemployment rates can also influence investor sentiment. Foreign investors may become cautious about investing in a country with a struggling labour market, fearing a lack of consumer demand and reduced profitability for businesses. As a result, they may choose to withdraw their investments or invest elsewhere, leading to a depreciation of the country's currency.
- Effect of High Unemployment on Exchange Rates:
The impact of high unemployment on exchange rates is often felt through market expectations and central bank policies. Persistent high unemployment can create an atmosphere of economic uncertainty, causing investors to anticipate potential interest rate cuts by the central bank. Lower interest rates tend to decrease the attractiveness of a country's currency to foreign investors, as they can seek higher returns elsewhere.
Also, high unemployment levels may also exert pressure on wages, limiting consumer spending and dampening economic growth. This reduced economic activity can further weigh on a nation's currency, as it signifies lower productivity and potential inflationary pressures.
- Correlation between Unemployment and Interest Rates:
Unemployment and interest rates share a complex relationship. Central banks often monitor unemployment levels to assess the overall health of an economy. When unemployment rises, it indicates a slack in the labour market, which can influence a central bank's decision on interest rates.
In response to high unemployment, central banks may adopt expansionary monetary policies, such as lowering interest rates, to stimulate economic activity and encourage job creation. By reducing borrowing costs, central banks aim to incentivize businesses to invest, expand, and hire more workers. These measures can potentially boost consumer spending, leading to a recovery in the labour market and a subsequent impact on currency values.
It's worth to know that unemployment rates and forex markets are intricately connected. High levels of unemployment can weaken a country's currency by reducing demand for its exports and prompting cautiousness among foreign investors. Furthermore, the impact of unemployment on exchange rates is often amplified by market expectations and central bank policies, which respond to labour market conditions. Understanding the relationship between unemployment, currency value, and interest rates can provide valuable insights for forex traders and investors looking to navigate these interconnected dynamics effectively.
Unemployment and Central Bank Policies
Role of Central Banks in Managing Unemployment:
Central banks play a pivotal role in a country's economy, primarily focusing on price stability and economic growth. While their primary mandate is to control inflation, central banks also recognize the importance of addressing unemployment. By implementing policies aimed at fostering a conducive environment for job creation, central banks indirectly contribute to reducing unemployment rates.
Monetary Policy and its Impact on Unemployment:
Monetary policy, controlled by central banks, involves managing the supply of money and influencing interest rates. Through these measures, central banks seek to regulate economic activity and stabilize financial markets. One significant way monetary policy impacts unemployment is by influencing borrowing costs for businesses and individuals.
When the central bank lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating investments and encouraging businesses to expand. This expansionary monetary policy can lead to increased job opportunities, as businesses may hire more employees to meet rising demands. Consequently, a lower unemployment rate may be observed due to the stimulating effects of monetary policy on economic activity.
Conversely, during periods of inflationary pressures, central banks may adopt contractionary monetary policies, aiming to reduce excessive economic growth. By increasing interest rates, central banks intend to curb borrowing and spending, thereby cooling down the economy. While this policy can be effective in curbing inflation, it may also lead to reduced business investments and slower job creation, potentially resulting in higher unemployment rates.
Employment Mandates of Central Banks:
Recognizing the significance of employment in overall economic well-being, many central banks have adopted explicit employment mandates. These mandates empower central banks to consider unemployment alongside price stability when making monetary policy decisions.
Central banks often monitor employment indicators such as the number of unemployed people, labour force participation rates, and data from the current population survey. By analysing these figures, central banks can gauge the health of the labour market and assess the effectiveness of their policies in promoting job creation and reducing unemployment.
It is important to note that while central banks can influence employment through monetary policy, they do not have direct control over job creation or the overall functioning of the labour market. Other factors such as fiscal policies, technological advancements, and global economic conditions also significantly impact employment outcomes.
We should know that unemployment remains a persistent challenge faced by societies worldwide. Central banks, while primarily tasked with maintaining price stability, have a role to play in managing unemployment through their monetary policy decisions. By carefully considering the impact of their policies on job creation, central banks can contribute to reducing unemployment rates and fostering economic prosperity. As we navigate the complexities of labour markets and evolving economic landscapes, central banks continue to refine their strategies to address the multifaceted issue of unemployment and support sustainable economic growth.
Unemployment and other Economic Indicators:
There exists a significant link between unemployment and various other economic indicators, which are crucial for understanding the health and performance of an economy. Two key indicators that showcase this relationship are GDP growth and inflation, along with the concept of the Phillips curve.
Firstly, when examining the connection between unemployment and GDP growth, it becomes evident that these two factors are often intertwined. GDP, or Gross Domestic Product, represents the total value of goods and services produced within a country during a specific time period. It serves as a measure of economic activity and can be influenced by the level of unemployment in a nation.
A higher unemployment rate often correlates with slower GDP growth. This relationship stems from the fact that unemployment indicates a significant portion of the working-age population is unable to find employment and contribute to economic output. When fewer individuals are employed, consumer spending power decreases, resulting in reduced demand for goods and services. As a consequence, businesses may experience lower sales and revenue, leading to a decline in overall economic growth.
On the other hand, a lower unemployment rate typically corresponds to higher GDP growth. When the labour force includes a higher percentage of employed individuals, there is an increase in disposable income, which can stimulate consumer spending. With increased consumer demand, businesses may expand operations, invest in capital, and hire more workers, thereby fostering economic growth.
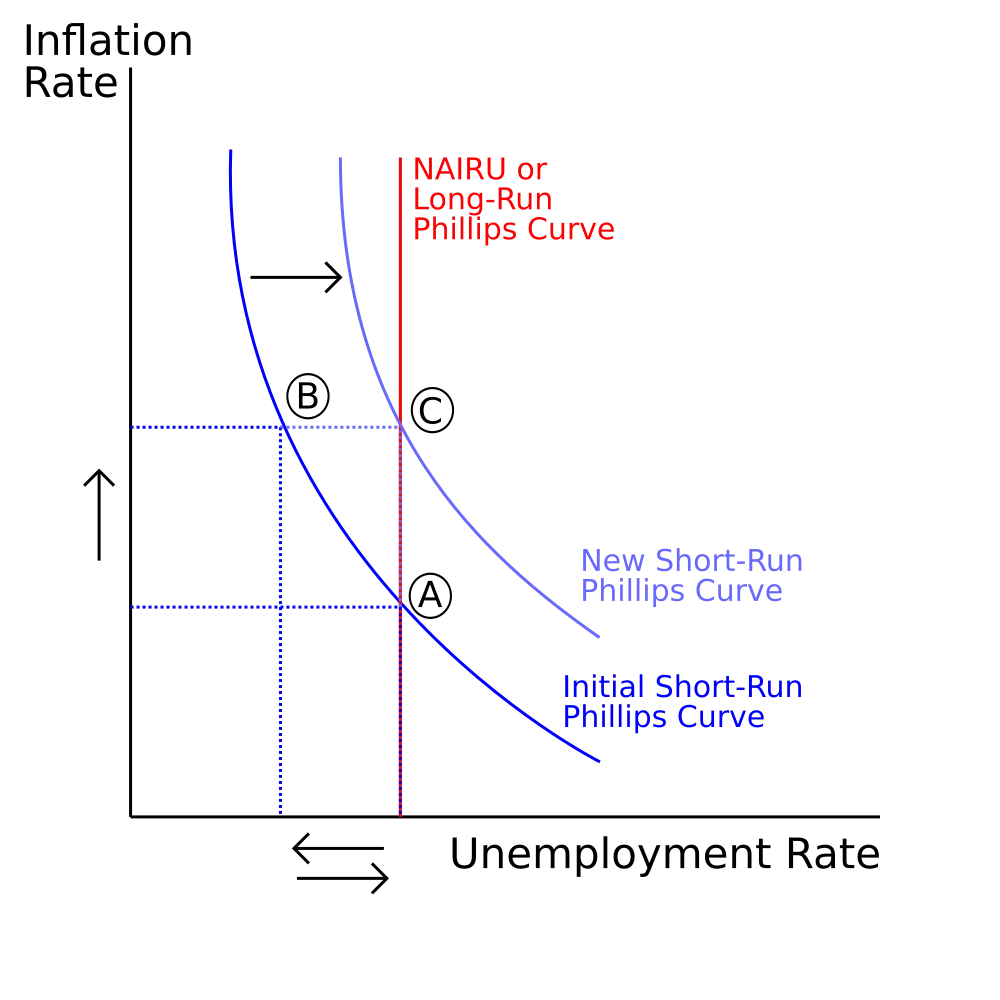
Another economic indicator that plays a role in the relationship with unemployment is inflation. Inflation refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over time. The Phillips curve theory suggests that there is a trade-off between inflation and unemployment—a phenomenon characterized by an inverse relationship.
According to the Phillips curve, when unemployment is high, there tends to be downward pressure on wages as there is a larger pool of workers available for a limited number of jobs. This leads to reduced spending power among individuals and weaker demand for goods and services. As a result, businesses may be compelled to lower their prices to attract customers, contributing to a lower inflation rate.
Conversely, when unemployment is low, the labour force experiences tighter competition for available jobs. This can lead to increased wage demands by workers, which can push businesses to raise prices to cover their higher labour costs. Consequently, inflation tends to rise in times of low unemployment.
It's important to note that the labour force also includes discouraged workers. Discouraged workers are individuals who have given up searching for employment due to various reasons, such as a lack of available jobs or unsuccessful attempts at finding work. While they are not included in official unemployment statistics, their presence can influence the overall employment situation and the relationship with other economic indicators.
In summary, unemployment is intricately linked to various economic indicators. The relationship between unemployment and GDP growth demonstrates how changes in the labour market can impact overall economic performance. Additionally, the trade-off between inflation and unemployment, as highlighted by the Phillips curve, sheds light on the inverse relationship between these two variables. By understanding these connections and considering factors such as discouraged workers within the labour force, policymakers and economists can make more informed decisions to address unemployment and foster sustainable economic growth.
Unemployment News and Data Releases: Insights and Market Implications
Key Economic Reports Related to Unemployment:
Several essential reports shed light on the current state of unemployment and its implications for the economy. Among these reports, the most notable are the monthly Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) report, the Job Openings and Labour Turnover Survey (JOLTS), and the Self-Employment Statistics.
The monthly Nonfarm Payrolls report, released by the U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics, provides valuable insights into the overall employment situation. It highlights changes in the number of employees across various sectors, including nonfarm businesses, government agencies, and nonprofit organizations. Traders closely monitor this report for indications of economic growth, as an increase in job creation often correlates with higher consumer spending and improved market sentiment.
The Job Openings and Labour Turnover Survey (JOLTS) measures the number of job openings available in the market. It reveals the level of demand for labour and reflects the overall health of the job market. When job openings rise, it suggests a robust labour market and potentially lower unemployment rates. Conversely, a decline in job openings may indicate a contraction in the job market, potentially affecting consumer confidence and spending patterns.
In addition to job openings, understanding self-employment statistics is crucial for a comprehensive analysis of unemployment data. Self-employment represents a significant segment of the labour market and can provide valuable insights into entrepreneurship, small business trends, and economic resilience. Monitoring self-employment figures allows traders to gauge the dynamism of the economy and its potential impact on consumer behaviour and market conditions.
Market Reactions to Unemployment Data Releases:
Unemployment data releases have a substantial impact on financial markets, particularly currencies and equities. Forex traders closely follow these announcements as they can significantly influence currency valuations. A better-than-expected unemployment report, such as a decrease in the total number of unemployed individuals, often leads to increased investor confidence in the currency of the respective country. This positive sentiment may result in a strengthening currency against other currencies in the forex market.
Conversely, if unemployment data reveals an unexpected rise in the total number of unemployed individuals, market participants may interpret it as a sign of economic weakness. Such news can trigger currency depreciation, as investors seek safer havens for their investments. Forex traders carefully analyse the data and assess its impact on interest rate expectations, monetary policy decisions, and overall market sentiment.
Interpreting Unemployment Data for Forex Trading Decisions:
When interpreting unemployment data for forex trading decisions, traders consider not only the headline figures but also the underlying trends and broader economic context. It's important to examine the data in conjunction with other key economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and consumer sentiment.
Positive trends in job openings, coupled with a declining total number of unemployed individuals, often indicate a robust economy with strong potential for growth. Such data can be favourable for the currency of the respective country and may present trading opportunities for forex market participants.
However, it's essential to consider the overall economic landscape and any potential factors that could influence future unemployment trends. Factors like technological advancements, geopolitical events, and government policies can significantly impact labour markets and alter the trajectory of unemployment rates.
Unemployment news and data releases hold substantial importance for traders and investors. By staying informed about key economic reports, monitoring market reactions, and interpreting unemployment data alongside other relevant indicators, forex traders can make more informed decisions.
Unemployment as a Leading Indicator:
One key aspect of using unemployment data as a leading indicator is its relationship with consumer spending. When unemployment rates are high, it often indicates a slowdown in economic activity and a decrease in consumer confidence. In such situations, individuals who are unemployed or fear potential job loss tend to reduce their spending, which, in turn, can have a negative impact on businesses and further contribute to economic decline. On the other hand, low unemployment rates typically suggest a strong labour force and increased consumer spending power, which can stimulate economic growth.
Employment data, including unemployment rates and job creation figures, also influence business sentiment indicators. Companies closely monitor employment trends as they provide valuable insights into the future demand for goods and services. When businesses observe a decline in the labour force, it may signal a potential decrease in demand, leading to a cautious approach in investment and expansion plans. Conversely, a growing labour force and declining unemployment rates can instil confidence in businesses, encouraging them to make strategic decisions for growth.
Overall, unemployment data acts as a leading indicator by shedding light on the health of the labour force and its implications for the broader economy. By understanding the relationship between unemployment and consumer spending, as well as its impact on business sentiment indicators, policymakers, economists, and businesses can make more accurate forecasts and strategic decisions to navigate the complex dynamics of the economy.
Unemployment and Risk Management:
Strategies to Mitigate Forex Risks and Currency Correlations
Unemployment is a critical economic indicator that not only affects individuals and societies but also poses risks for businesses and financial markets. By incorporating unemployment data into risk assessment models, businesses can gain valuable insights and develop effective strategies to mitigate forex risks, understand currency correlations, and optimize diversification. This section explores the significance of unemployment in risk management and discusses hedging strategies that can help navigate the challenges associated with unemployment-induced currency fluctuations.
Incorporating Unemployment Data into Risk Assessment Models:
Risk assessment models play a crucial role in identifying potential vulnerabilities and evaluating the impact of various economic factors on business operations. By incorporating unemployment data, these models can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the risks associated with currency fluctuations. Unemployment rates can serve as leading indicators of economic health, reflecting the overall employment situation and consumer confidence. By monitoring and analysing unemployment trends, businesses can anticipate potential shifts in demand, economic growth, and market sentiment, enabling them to adjust risk exposure accordingly.
Hedging Strategies to Mitigate Forex Risks Associated with Unemployment:
Unemployment can significantly impact foreign exchange (forex) markets, leading to heightened currency volatility and increased forex risks. To mitigate these risks, businesses can employ various hedging strategies. One commonly used strategy is currency hedging, where businesses enter into financial contracts, such as forward contracts or options, to protect themselves against adverse currency movements. By hedging their forex exposures, businesses can minimize potential losses caused by sudden shifts in exchange rates influenced by unemployment-related developments.
Another effective strategy is diversification, whereby businesses spread their forex risks across different currencies and markets. This approach helps reduce the vulnerability of a business's portfolio to unemployment-driven currency fluctuations in specific regions or economies. By diversifying their forex holdings, businesses can attain a more balanced risk profile and potentially offset losses in one currency with gains in another. Diversification can also help mitigate the negative impact of unemployment-induced currency correlations, as it reduces reliance on a single currency or market.
Impact of Unemployment on Currency Correlations and Diversification:
Unemployment has a notable impact on currency correlations, which refer to the statistical relationships between currency pairs. During periods of high unemployment, currency correlations may strengthen due to shared economic factors and market sentiment. This increased correlation implies that currencies move in similar directions, making it challenging for businesses to achieve effective diversification solely through currency exposure.
Understanding the impact of unemployment on currency correlations is essential for risk management. By considering unemployment data alongside other economic indicators, businesses can gain insights into potential shifts in currency relationships. This knowledge allows them to adjust their diversification strategies and identify currency pairs that may provide better risk-reducing benefits during periods of unemployment-induced market volatility.
 Balance Guard
Balance Guard